How do you know if your warehouse is well organised? For that, you need to put the following two questions under the magnifying glass: “Is the flow of goods optimal?” In other words, does everything get where it needs to be quickly, without delay. And: “Are your goods stored in efficient racking?” I.e. are your racks and shelving optimally adapted to your products. Let’s start by looking at the different storage and flow methods. Because smart storage does wonders for your workflow.
1. The two basic methods of storing goods
► Option 1: the ABC method
The ABC method is a common reasoning for storing goods in a rack. The formula behind it takes into account the turnover rate of your goods. The higher the turnover rate (and therefore the more often a product is sold), the easier it should be for your warehouseman to remove that product from the shelves. It is then best to place those products at picking height, nicely in the middle of your rack. The turnover rate of your goods is calculated using this formula: Turnover in pieces / Average stock in pieces
Using the figures from that calculation, you then classify your products:
-
Category A corresponds to about 20% of your references. Together, they represent on average 80% of all rotations. These popular products should therefore be at grab height of your order pickers.
-
Category B comprises 30% of your references (and ± 15% of your rotations). These products are less frequently removed from stock and you may therefore store them at the bottom of the shelf.
-
Category C corresponds to 50% of your references and only 5% of your rotations. The products in this category are the least popular and are therefore best placed on the top shelves.
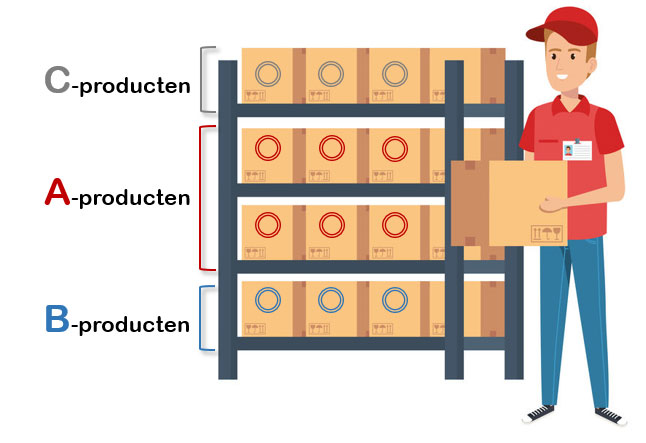
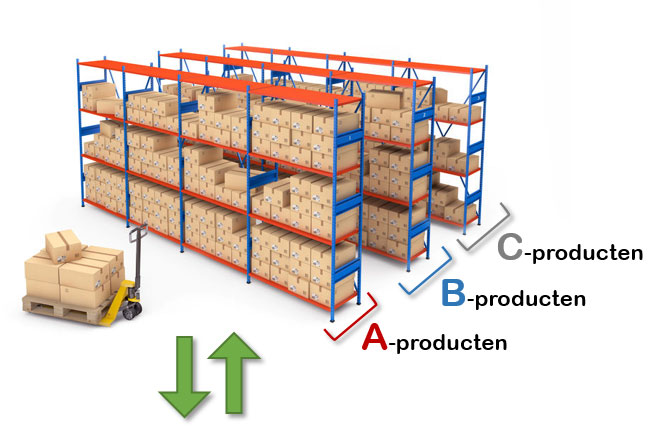
By the way, you can apply the same ABC method to the entire layout of your warehouse. You then store your category A products close to the packing tables. The further you move away from the packing tables, the less popular your products become. First you still have the B-products, and at the very end, finally, the C-products.
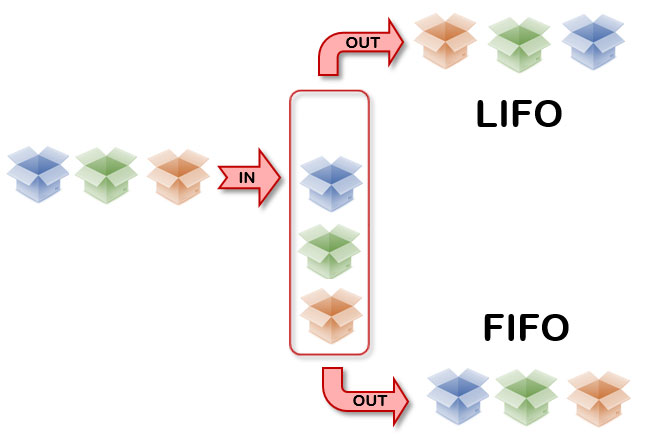
► Option 2: the LIFO and FIFO method
Both these methods may be opposites, but they share the same basic reasoning. The LIFO method stands for Last In – First Out. According to this type of layout, the products that were placed last in your warehouse are also taken out first. Compare it to a stack of trays, where the tray that is placed on the stack last is usually also the first tray to be taken off.
Related to this is the FIFO method: first in – first out. This is the opposite principle. So the products that are stored first also leave first. Ideal if, for example, you work with products where there is an expiry date. Naturally, you want to get these out of your warehouse as quickly as possible.
- When picking manually, it is sufficient to leave a few centimetres of free space above and between your stored goods/boxes.
- When picking by machines, it is recommended to keep at least 10 centimetres of free space (both along the top and both sides).
► Conclusion: which storage method is right for you?
The method most often used is the ABC method. It is the most efficient storage technique with the lowest movements and efforts for your warehousemen. If you sell products with an expiry date, opt for the FIFO model. The oldest products are then put back on the market first.
And what do we do at RAJA? We start from the ABC method: the 1,000 most popular articles are closest to the packing tables. The further you step away from our packing tables, the lower the turnover rate of these products. Linked to this, we also apply the FIFO method: products older than 100 days are taken out of the warehouse first. So you see, combinations of different storage methods are perfectly possible!
]2. Choose the right racking for the best storage
Thanks to some well-thought-out letters of the alphabet, we have been able to determine the best order in which to store goods. In this second part, we look at five storage systems, all tailored to your products or needs. Which type of racking will it be for you? You will find the most common racking systems for an average warehouse in the selection guide below (PDF download):
► Option 1: shelf racking
This rack is for (small) products with a high turnover rate. For those using the FIFO method, this can be very handy. Your products with the highest turnover rate should be stored at grab height. The rest of your products are then placed above or below. When using a rack, it is advisable to store the heavier products at the bottom. The higher up in the rack, the lighter your products will be. Finally, limit the height of your racking to around 2 m. This is easier for your warehouse staff to work with.

► Option 2: mezzanine storage
]Here you follow the same principle as the previous option, except that your warehouse is divided into two floors. An area can be created on each mezzanine floor to place racking. As you make better use of your available storage space in height, more space is left between the racks. This is needed to ensure smooth circulation of pallet trucks, for example. Remember to correctly demarcate this type of storage area with floor markings and protective barriers.

► Option 3: modular shelving
]This rack is especially suitable for products that are difficult to transport on a pallet. For example, pipes, bars, carpets, etc. It also comes in handy when storing products that are seasonal, and where storage capacity can therefore fluctuate a lot throughout the year. Depending on the model, up to three racks of this type can be stacked on top of each other. There are variants suitable for indoor use or outdoor use (thanks to their galvanised steel finish).

► Option 4: pallet racking
For a B2B company, this is the most recommended storage method. This is because it is best suited to storing large quantities of goods. These are often stacked on pallets. Here, the pallets rest on strong beams. These can support weights of up to 3,000 kg per level. It is best to install suitable metal barriers around your pallet racking. This gives your racks and goods optimum protection against knocks from rolling stock.

► Option 5: storage in‘narrow aisles‘
If you have a warehouse where you can work at height without too many obstacles, opt for ‘narrow aisle’ storage. In these storage units, the distance between the racks is just wide enough for a special picking machine. That picking machine has a very large lifting height. This type of storage is particularly useful when you want to store a large mass of small products in a limited area. You can thus make maximum use of the available height.

Watch the video below and find out how we applied the principle of narrow corridors at RAJA:















