Strapping straps: these are those strong ‘ribbons’ you see quite often around boxes or pallets. They keep goods tightly packed and are therefore an indispensable link in cargo securing. And for those who might be in doubt: you are spoilt for choice when it comes to types and versions. So how do you know which type suits your cargo best? You will find the answer to that question in the selection guide below. We also give you tips on accessories, machines and techniques to make strapping run smoothly.
1. What strapping straps exist?
Based on the raw material, we can distinguish 5 types of strapping: paper, polypropylene (PP), textile, polyester and steel. Each type has its own advantages, of course. For example, polypropylene strapping is the cheapest (and most popular) variant in the packaging world. It is made of a type of plastic with an embossed structure for better grip. The strongest type, in turn, is steel strapping: ideal for the construction industry, for example. You can compare all types of strapping in the table below:
| Material |
Applications |
Properties |
Paper |
. – For very light goods. – For short-term use (indoors only). – For manual or machine strapping. |
. – Tensile strength up to 55 kg. – Environmentally friendly: 100% from renewable raw materials. |
Polypropylene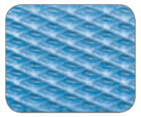 |
. – For light goods. – For short-term use (indoors only). – For manual or machine strapping.1 |
. – Tensile strength up to 245 kg. – With embossed surface.2 – Most elastic. |
Polyester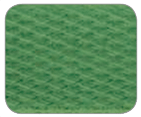 |
. – For heavy goods. – For long-term use (indoor/outdoor). – For manual or machine strapping.1 |
. – Tensile strength up to 534 kg. – With embossed surface.2 – Resists sharp edges. |
Textile |
. – For very heavy or fragile goods – For long-term use (indoor/outdoor). – For manual strapping. |
. – Tensile strength up to 820 kg. – With soft surface. – Resists sharp edges. |
Steel |
. – For very heavy goods. – For long use (indoor/outdoor).3 – For manual strapping. |
. – Tensile strength up to 775 kg. – Resists sharp edges. – Least elastic. |
1 Depending on the quality of the strapping. Download this selection guide (PDF) for a complete overview.
2 Relief surface: provides more grip on the substrate and guarantees a stronger seal when welding. The relief also makes the strapping more flexible and resistant to tearing.
3 Always use ‘painted’ steel strapping for outdoor use (= better resistance to corrosion, among other things).
- Why is it best to use PP-band only in the short term? PP tape is much more elastic than other types. After stretching, the tape will want to recover to its original length. However, PP-band tends to 'relax' (i.e. stretch) after a while. It then loses some of its elasticity (± 35% after 2 weeks). This makes it less effective in the long term.
- Why is it best to use PP tape indoors only? PP tape is less resistant to UV light. That light is detrimental to the quality and colour. White bands in particular suffer from this
2. What are the applications of strapping?
First, let’s look at the definition of strapping. Strapping straps are used to close, secure or group goods. The intention is to stop your cargo from moving during transport. Strapping facilitates transport and makes it safer to move pallets, among other things. Depending on the material, you can use strapping for the following applications:
- Paper strap
 : to be used for applications for which you used to need, for example, plastic wrapping film such as strapping packages, bundling and grouping products, etc. The paper tape is also an environmentally friendly alternative to PP tape with limited tensile strength.
: to be used for applications for which you used to need, for example, plastic wrapping film such as strapping packages, bundling and grouping products, etc. The paper tape is also an environmentally friendly alternative to PP tape with limited tensile strength. - Polypropylene strap: bundling of newspapers or magazines, extra protection against theft for light packaging, closing cardboard boxes or crates, reinforcing (light) pallet loads, etc.
- Polyester strap: for palletising medium to heavy loads, grouping tubes, etc.
- Textile strap: strapping goods with fragile surfaces (such as wood) and objects with protruding or pointed corners (such as boards and tiles), etc.
- Steel strapping: suitable for securely strapping very heavy, sharp and round loads such as building materials.

3. Manual strapping: how to do it?
Strapping by itself is not enough to get started. How do you tighten your strap and what do you use to fasten the ends? For that, some additional tools are just around the corner… We first show you how best to strap manually. It is without doubt the most economical solution. In doing so, you need to use one of these basic tools: buckles or seals.
Good to know: a buckle is only suitable for a PP (polypropylene) or textile strap. A seal can be used for PP, polyester or steel bands. Would you like more information about manual strapping? You can! Download our free selection guide here (PDF).
Buckle + Strap tensioner |
. Make 2 loops in the strap and attach it in the buckle. After this, tighten it by hand or with a strap tensioner. Simple and effective! ⇒ Suitable for paper, PP or textile strap. Watch our instruction video here. |
Seal + Tensioning pliers |
. Step 1: place a seal and your strapping band in the pliers. Step 2: tighten the strapping band with the tensioner. Step 3: the seal is then clamped and the strap cut off. Done! ⇒ Suitable for PP, polyester or steel strapping. Watch our instruction video here. |
 Did you know that… you can also manually strap using paper strapping? You then best combine your strap with plastic buckles.
Did you know that… you can also manually strap using paper strapping? You then best combine your strap with plastic buckles.
4. Machine strapping: how to do it?
For strapping larger quantities, it is best to stop at a strapping device or machine. With such a machine, the ends of your strapping are welded together. This gives you the strongest seal without a doubt. Would you like to know what options are available for machine strapping? Then download our free selection guide here (PDF).
Good to know: when strapping by machine, it is best to use a plastic strap with an embossed structure (PP or polyester). Always place the side with the deepest relief upwards in the machine. This allows the strapping to melt and adhere better. Another thing not to lose sight of is… eye protection. Always wear safety goggles and gloves when applying and cutting strapping. Safety first!
Strapping device |
These devices have the highest working capacity (up to 150 strappings per hour) and can be used vertically and horizontally. Good to know: strapping devices also work ‘in the air’. So the device does not necessarily have to rest on a flat surface. |
Strapping machine |
. Ideal for strapping loose parcels and boxes. All you have to do is hang the strapping band around the parcel. The sealing and cutting of the strap are done automatically. |
 Did you know that… you can also do machine strapping with paper strapping? It is best to use a machine from this list.
Did you know that… you can also do machine strapping with paper strapping? It is best to use a machine from this list.
5. Which accessories come in handy when strapping?
- Corner profiles: when strapping pallets, there is a great deal of tension from the strapping band on your goods. To prevent the strap from cutting into your goods, use a corner profile. It protects and gives more stability to your pallet load. They also keep your strapping in place better.
- Corner protectors: a corner protector is only used at those corners where the strapping can cut into your goods. Ideal for smaller packages.
- Steel strap shears: this type of shear holds the strapping securely while cutting, eliminating the risk of ‘slipping off’ and injury.

- Mobile reel: a reel makes it much easier to move and unwind a roll of strapping. In addition, there is often a tray for extra tools.
- Pallet needle: slide the pallet needle under your pallet and apply the strapping band much more easily. Bending down is no longer necessary and your back will be happy about that.