This career began almost 90 years ago as a “container for rolls of adhesive tape with dry adhesive“. Today it is impossible to imagine warehouses, logistics, shipping, production, offices, and households without it: we are talking about adhesive tape! After the name tesa® was originally given to a toothpaste and even a sausage pellet, Beiersdorf applied for a patent for the transparent adhesive roll and the accompanying table dispenser in 1936. This is the beginning of an indescribable triumphant advance of the adhesive tape, the areas of application are now almost inexhaustible: as a sealant, as an insect trap, warning tapes to mark stair treads, double-sided adhesive strips to hang posters up to entire shelves – people are sticking for all they are worth. And the best thing is: it lasts!
But which tape is the right one? In the following, we will explain the types of adhesive tape and materials, as well as the properties of the various adhesive tapes and explain what adhesive tapes are made of, which tape is best suited for which purpose and which adhesive tapes are the right ones for packaging.
What you can expect in this blog article:
- Which tape is the right one for packaging
- How to use adhesive tape correctly to seal shipping boxes
- Common problems when packing with tape
- The right way to store tape
- Printing your own tape
Adhesive tape material
The structure, components and technical properties are decisive for the quality of an adhesive tape and determine which tape is suitable for which application.
The structure of an adhesive tape
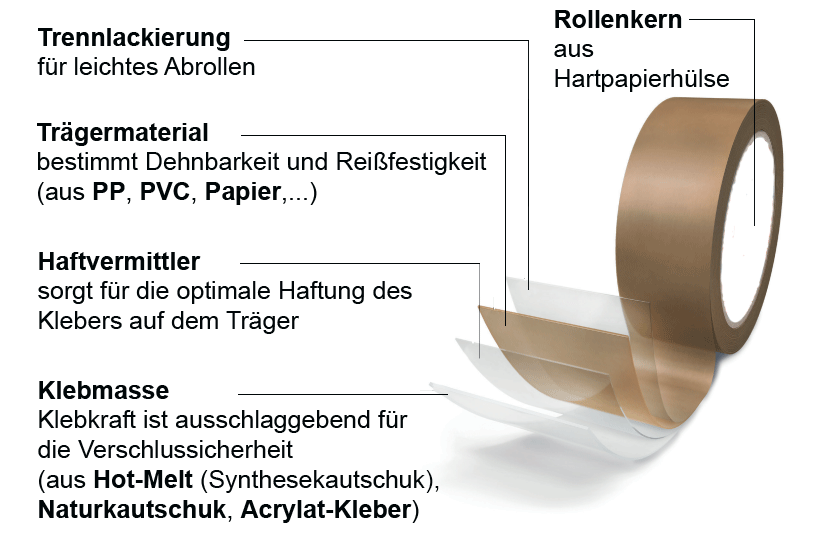
The two essential components of an adhesive tape are the backing materialwhich is decisive for the tear strength and stretchability/flexibility of an adhesive tape, and the adhesive or the adhesive mass, which determines the adhesive properties, such as adhesive strength, immediate adhesion or durability.
Some types of adhesive tapes, especially PP adhesive tapes, also have a release coating and an adhesion promoter:
- The release coating is located on the outside of the backing. It ensures that the tape can be easily unrolled from the roll without sticking.
- The adhesion promoter, also called primer, is located between the backing and the adhesive and ensures optimal anchoring of the adhesive mass to the backing material. Many plastics have a low surface energy, which means that the adhesive has difficulty adhering to them. The bonding agent increases the surface tension, which causes the adhesive to adhere more strongly to the backing.
- With double-sided adhesive tapes, both sides of the backing material are coated with adhesive and the tape has an additional, removable silicone-coated release liner on top of the closed adhesive mass.
Substrates of adhesive tapes
The backing material has the task of carrying the adhesive mass and the bonding agent. It thus also determines the tear strength and stretchability of an adhesive tape. Where, how long, on which surface and for which purpose the tape is used determines which backing material is suitable.
The most common types of adhesive tape for packaging are film tapes made of PP (polypropylene backing) or PVC (polyvinyl chloride backing) and paper tapes (paper backing). In addition, there are other backing materials such as cotton, non-woven and viscose for fabric tapes and metal (e.g. aluminium adhesive tape) for adhesive tapes that are primarily used in industry, trade and construction.
|
PP |
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) |
Paper |
|
Advantages
|
Advantages
|
Advantages
|
|
Disadvantages
|
Disadvantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
Range of application
|
Range of application
|
Range of application
|
*Wet adhesive tape is a packaging tape made of paper with an odourless adhesive (plant glue) that is activated with water. This creates such a strong bond that the tape cannot be removed from the cardboard without being seen. The tape is recyclable, insensitive and holds even on dusty surfaces. It can only be used in conjunction with a manual or electronic tape dispenser with a water reservoir that moistens and cuts the tape strips. In our blog article on paper packing tapes we explain the advantages of wet and paper tape.
Filament tape or filament-reinforced packaging tape is a PP packaging tape with hot-melt adhesive that is reinforced with longitudinal glass-fibre threads and is therefore very tear-resistant. It has a high immediate and permanent adhesion. It is used when shipping hazardous goods and is also suitable for heavy export shipments. Read more about the benefits of filament in the Filament Reinforced Tapes blog.
Other backing materials of adhesive tapes for industrial and craft applications
Adhesive tapes are not only needed for packaging, but also in industry and crafts, different types of adhesive tapes are used for different purposes:
Fabric tape is tape reinforced with textile fabric or tear-resistant plastics (PET). It is very durable, has a high tensile strength, but at the same time can often be torn by hand. It is therefore very suitable for bundling, sealing or insulating. The best-known example is Gaffa tape .
Crepe tape is used for masking during painting or cleaning and for special applications in production. However, it has become best known for its use in the craft sector, mainly by painters. Masking tape is excellent for masking walls or for defining straight lines and sections when painting. Crepe tape has hot melt (cheap quality) or natural rubber adhesive (high quality) and is made of crepe paper (also called flat crepe). Painted parts are often heated to high temperatures in ovens. Therefore, crepe adhesive tapes must be heat-resistant. Adhesive crepe tapes can be removed without leaving any residue.
Adhesive tapes with metallic backing material are mostly used where electronics are involved. Due to their ageing and temperature resistance and their ability to conduct electricity, they can serve as a heat barrier in electrical equipment. An example: aluminium adhesive tape
Adhesive types and their advantages/disadvantages
There are 3 adhesives that are most commonly used for the adhesive mass of an adhesive:
Hot-Melt
Hot-melt adhesive is used for PP packaging tapes. As the name suggests, it is a synthetic hot-melt adhesive. This means that the synthetic adhesive granulate is melted by heating and applied to the backing material at a temperature of approx. 90 °C.
Suitable for light to medium weight cardboard boxes, for short storage and shipping.
Advantages:
- high initial tack (sticks quickly and adheres immediately)
- cost-efficient
- good sealing performance under normal conditions
- good adhesion to steel
- easy to roll off
Disadvantages:
- low UV and ageing resistance (max. half a year)
- Loud rolling noise
- temperature sensitive
Acrylic adhesive
Acrylic adhesive is a synthetic adhesive in which the raw materials are dissolved in a water dispersion. This dispersion is applied to the carrier film and the liquid is evaporated in an oven. Acrylic adhesives are significantly more powerful than natural rubber or synthetic rubber adhesives
Suitable for light to medium-weight cardboard packaging, for longer transport distances without climatic fluctuations
Advantages:
- Easy to roll off
- High transparency and ideal for white cardboard
- Continuous adhesion and good tack (especially suitable for long distance transport)
- Suitable for extended storage and outdoor use due to high UV and ageing resistance (max. 1 year)
Disadvantages:
- Weak initial tack
- Temperature sensitive
- Limited suitability for recycled cartons
Natural rubber
Natural rubber adhesive consists of 97% natural rubber and approx. 3% solvent. Natural rubber is the most environmentally friendly adhesive option and is considered the highest quality adhesive material on the market.
Suitable for medium and heavy cardboard boxes, also for export goods and transport through different climatic zones. Suitable for storage in deep-freeze areas.
Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly
- Wide range of applications due to many variants of strong and weak adhesives
- High adhesive strength, fast adhesion, faster and stronger hold than other adhesives
- Good temperature resistance (suitable for freezing)
- Quiet unrolling (well suited as machine tape)
Disadvantages:
- Low UV and ageing resistance (max. half a year).
- Colour differences possible due to natural product
- Adhesive turns yellow during longer storage
Why does adhesive tape stick? Technical properties of adhesive tape
The following terms from adhesive technology play a role in particular for the quality and thus also for the comparability of adhesive tapes. In standardised test procedures, these properties of adhesive tapes are tested so that they comply with the applicable standards:
The adhesive force, also called peel force or peel adhesion, is the force required to remove an adhesive strip from a bonded substrate . This indicates the quality of the adhesive strip in relation to its purpose. According to DIN standard EN 1939:2003, the adhesive force is measured under laboratory conditions on polished steel. The adhesive strips are pulled off in a certain width (10, 25 or 50 mm) under predefined conditions (defined pressure force, tearing speed and angle). Depending on how much force has to be applied to release the adhesive strip from the substrate, the adhesive force is then divided into 3 gradations, whereby the value is given in Newton per mm.
For a 25 mm wide adhesive tape, the following average values apply accordingly:
- Low (weak) adhesive force: < 3.75 N/ 25 mm
- Medium adhesive force: approx. 3.75 to 7.5 N/25 mm
- High (strong) adhesive force: > 7.5 N/ 25 mm
- The adhesive strength is generally better on smooth surfaces than on porous, rough and uneven surfaces.
- The adhesive strength depends on the properties of the backing material (stiff, flexible), the contact pressure, the adhesive and the ambient temperature: rubber adhesive, for example, liquefies under the influence of heat, which significantly reduces the adhesive strength.
- When buying adhesive tapes, never only pay attention to the adhesive strength, because a high adhesive strength does not mean that the adhesive tape can adhere everywhere, as the adhesive conditions and the substrate to be bonded are just as decisive for a good adhesive result.
The 3 forces that act together within a pressure-sensitive adhesive are decisive for the adhesive strength:
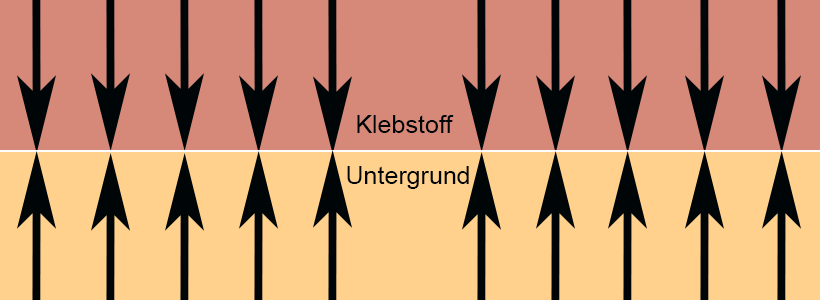
- Sometimes it is an advantage if the tack is not so high, for example if you want to correct the position of the tape again or if the tape is only to adhere to the surface for a short time and then be removed again without leaving any residue. Painter's masking tape is a classic example of a tape with low tack.
- Caution: A tape with weak instant tack can still have excellent final tack.
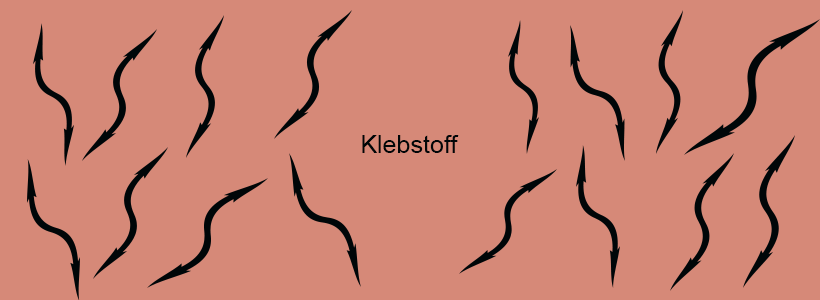
- A high cohesion is necessary, for example, if the adhesive strip is to be removed without leaving any residue; the high cohesion ensures that the molecules in the adhesive are firmly bonded to each other and thus do not "tear apart" when removed. Adhesives with low cohesion often leave adhesive residue on the surface after removal. Adhesive tapes with high cohesion are therefore for bonding that is only temporary, e.g. on sensitive surfaces.
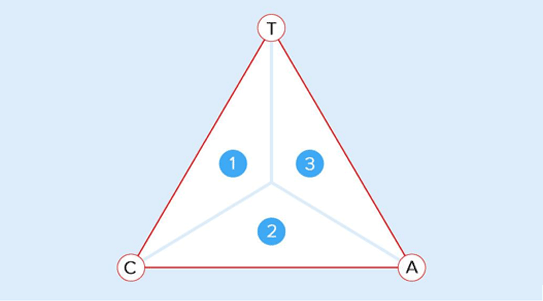
1) Temporary and reversible bonds: depend on cohesion and tack, adhesion is of secondary importance, as the bond is to be released again.
2) Permanent bonds: Cohesion and adhesion are paramount. The strength of the bond is crucial. How strong the bond is at the first moment is secondary.
3) Quick-stick bonds: the adhesive bond must be made quickly.
High tensile or tear strength is particularly important for single-sided packaging tapes, especially for packaging and transport securing tapes that need to hold heavy loads in place during transport. Tensile strength is the force/load required to tear the tape. It is measured in Newtons per cm (N/cm) by pulling a 1 inch wide tape in the opposite direction at both ends until it tears.
The same procedure is used to measure the elongation at break or elongation at tear. It is the percentage by which the tape can be elongated before it breaks. The elasticity of the backing material is crucial here. Elastic adhesive tapes such as fabric tapes usually have a high elongation at break because they are often used on irregular rounded surfaces.
Tape thickness is often given in µ and refers to the total thickness of the tape without the release liner. The thicker the tape, the more puncture resistant it is – thick tapes are, for example, repair tapes that are valued for their high rigidity. The disadvantage is that they are not very conformable and not very flexible.
Temperature range/span describes the property of the adhesive tape to withstand certain temperatures after bonding without reducing the bonding performance. The temperature range is given in °C from the lowest cold degree to the highest. Often, as temperatures rise, the tackiness of an adhesive also increases, whereas the adhesive strength decreases. When temperatures drop, the tackiness decreases accordingly.
The ageing resistance indicates how long an adhesive tape is durable, i.e. how long it can be used without loss of adhesive strength.
Which tape is the right one for packaging
When tape is used for packaging purposes, it is referred to as packing tape. For us as a packaging mail order company, the focus is clearly on sealing cardboard boxes. Using the right packing tape ensures that the packaging is properly sealed and the products can be transported undamaged. Several factors play a role in choosing the right packing tape:
- The surface of the materials to be taped – Which carton/quality of carton (kraftliner/testliner) will be sealed with the tape?
- What is the weight of the packaged goods?
- The type of transport and storage – Which climatic conditions and environmental influences is the adhesive tape exposed to (of particular interest in deep-freeze areas or when exporting to tropical countries)?
- The duration of the adhesion
- Does the unwinding behaviour and the unwinding noise play a role (there are indeed tapes that are easy to unwind and those that are difficult to unwind, or tapes that are loud or quiet)?
- Optics/safety/environment
Which tape types for which carton quality
Cardboard boxes come in many different types and sizes. Often the corrugated cardboard from which the cartons are made is made from so-called recycled fibres/testliner, i.e. recycled material. As it stands, paper fibres can be recycled up to seven times before the fibres become too short for use, new research shows that in the future it might be possible to recycle them up to 25 times with high quality!
For boxes with recycled fibres we recommend PVC or paper tape with natural rubber as the adhesive as it sticks better to the substrate. PP hotmelt works for smaller cartons with low weight.
There are also cartons that contain recycled fibres on the inside and “new” fibres/ kraftliner on the outside. New fibres are then obtained from fresh pulp. This combination of different papers usually results in a slightly stronger carton. There are also cartons made entirely from kraftliner/new fibre. If the cartons have new fibres, almost any type of tape can be used, then the choice depends more on the size and weight of the contents.
To ensure that the tape used does not leave any unwanted residue, it is important to determine in advance what surface the tape will be stuck to. If, for example, a move is planned and wooden furniture or even glass is to be fixed with adhesive tape, then PVC adhesive tape or adhesive tape with natural rubber adhesive should be used. With other adhesives, such as acrylate or hotmelt, there is a high risk that the tape cannot be removed without leaving residues.
How to use adhesive tape to seal shipping cartons correctly
Many people are still of the opinion that a lot helps a lot! Often, the package is literally wrapped in adhesive tape. A consumption of material that is not necessary.
We show three types of closure that can be used to securely seal cartons with the least amount of material possible, depending on the contents of the carton and the transport distance:
U-shaped closure
The butt edges of the lid and the bottom are each provided with a length of adhesive tape
Suitable for light packaged goods up to 20 kg with short transport distances without high loads.
Combined U- or L-shaped closure
In addition to the butt edges, the side edges are also sealed with packing tape
Suitable for medium to heavy packages up to 40 kg with a short transport route or long storage time
H-shaped closure
The most secure type of closure - the edges of the box are taped to stabilise the box and protect it from moisture.
Suitable for heavy packages over 40 kg with long transport distances and long storage times
When working with adhesive tape, temperature also plays a major role: it is best to process the tape at a temperature of at least 10 °C; in colder environments PP packing tape with natural rubber adhesive or wet adhesive tape is more suitable, and in warmer environments PP packing tape with acrylic adhesive or wet adhesive tape.
It is best to use an adhesive tape dispenser to seal the cardboard boxes with packing tape. Apply slight pressure to the tape, but avoid strong stretching. If many cartons have to be sealed, automated carton sealing machines that can be integrated into packing lines are also suitable.
Common problems when packing with packing tape
The tape tears during processing
- never open the packaging of adhesive tapes with knives, the smallest damage to the tape leads to tears during processing.
- Check dispenser
The packing tape does not hold on the carton
- Check the dispenser and remove any dirt if necessary.
- Make sure the tape is stored correctly
- Check if the tape fits to the surface of the carton (on test liner for example use tapes with hotmelt or natural rubber glue).
The packing tape does not stick to the carton during transport.
- Check the sealing technique
- Possibly it has to do with climatic fluctuations during transport, the packing tape can lose its adhesive strength – adhesive tapes with acrylate adhesive are very temperature-resistant and can remedy this.
The box opens again despite the packing tape
- Multi-wall cartons have a higher lid flap tension, they may need a stronger packing tape, such as a PVC tape or a thread-reinforced tape A different sealing technique (e.g. the H-seal) can also provide a remedy
- use thread-reinforced tape
- Change carton quality
The correct storage of adhesive tape
Packing tape should be stored horizontally, at a constant temperature between 12-23 degrees and in the dark. It is best to store it in the packaging in which it was delivered to protect it from dust. Always make sure to use the oldest adhesive strips first, as tape has a limited shelf life. If the tape gets too hot or too cold, it is best to leave it at room temperature for 24 hours before use. Half a year’s storage is not a problem, PP tapes with acrylic adhesive can be stored for up to a year, wet adhesive tape even for several years. It is important to protect the tapes from UV radiation, dust and moisture.
Print your own adhesive tape
With the adhesive tape configurator, anyone can design their own packaging tape online with a logo and have it printed. This has many advantages:
Personalised packing tape is one of the easiest ways to get the word out about your business. The shipping packaging is securely sealed, represents the brand at the same time and acts as an advertising medium. Read our blog articles on the benefits of personalised tape.

Conclusion
Which adhesive tape is the right one depends very much on the purpose and the conditions of use. We are happy to help and advise you in your choice!
















