Adhesive tapes are indispensable in many industrial and trade applications. However, not every adhesive tape can withstand extreme temperatures. High heat or extreme cold can significantly impair the adhesive strength, which can lead to material failure and safety risks. It is therefore crucial to choose the right cold-resistant or heat-resistant adhesive tape for the respective area of application.
Typical areas of application for heat and cold-resistant adhesive tapes
- Industry & mechanical engineering: Fastening in high-temperature areas or cold production environments
- Electrical engineering: Insulation of cables and circuit boards under extreme temperatures
- Automotive industry: Protection of components exposed to hot engine conditions or frosty outside temperatures
- Construction & trade: assembly and sealing under changing weather conditions
- Aerospace: Protection against extreme temperature differences at high altitudes or in space
This article shows which materials are particularly suitable for heat-resistant adhesive tapes, cold-resistant adhesive tapes and temperature-resistant adhesive tapes and what to look out for when selecting them.
Basics of temperature resistance
How temperatures influence adhesive strength
The adhesive strength of an adhesive tape depends heavily on its chemical composition. High temperatures can make the adhesive too soft, causing it to lose its adhesion. Low temperatures, on the other hand, can harden the adhesive, causing it to become brittle and no longer adhere.
Short-term vs. permanent temperature exposure
There is a big difference between short-term exposure to heat (e.g. during a soldering process) and long-term exposure to heat (e.g. in an engine compartment). The same applies to cold: some adhesive tapes can withstand very low temperatures for a short time, but lose their flexibility when exposed to cold for longer periods. In our article, we refer to the load limits under permanent temperature exposure. For example, polyimide adhesive tape (also known as Kapton® ) can withstand temperatures of up to 400 °C in the short term – but has a long-term temperature resistance of up to 300 °C.
Important physical and chemical properties
We have compiled useful information on the behaviour of certain materials under heat, in particular the temperature resistance of plastic, in another blog article. The most important key figures here are:
- Melting point of the materialDetermines when the adhesive becomes too soft and the carrier material begins to melt
- Glass transition temperature (Tg): Point at which the adhesive becomes brittle
- Resistance to UV radiation and moisture: Important for outdoor use
Why is the glass transition temperature (Tg) important for adhesive tapes?
The glass transition temperature (Tg ) refers to the point at which an amorphous or semi-crystalline material – such as plastics, resins or adhesives – changes its state: From hard and brittle (glassy) to soft and rubbery (viscoelastic). The Tg has an influence on the carrier material and the adhesive of an adhesive tape:
The adhesive strength of adhesives depends heavily on the Tg:
- An adhesive with a high Tg remains firm & stable → good for heat-resistant applications.
- An adhesive with a low Tg remains flexible even in cold conditions → ideal for cold-resistant applications.
- Is the Tg too high for the application? → The adhesive could become brittle and crack at low temperatures.
- Is the Tg too low for the application range? → The adhesive could become too soft at high temperatures and lose its adhesive strength.
Examples of the glass transition temperature (Tg) of different substrates:
| Material | Tg (glass transition temperature in °C) |
|---|---|
| polyimide | approx. 360 °C |
| PTFE | approx. 120 °C |
| PVC | approx. 80 °C |
| Acrylic adhesive | approx. -40 °C to +10 °C (depending on composition) |
| Silicone adhesive | approx. -100 °C to -50 °C |
| Rubber adhesive | approx. -60 °C to -40 °C |
Note: The lower the Tg, the more flexible the material remains at low temperatures.
Examples of the glass transition temperature (Tg) of adhesives:
| Adhesive type | Glass transition temperature (Tg in °C) | Properties & areas of application |
|---|---|---|
| Acrylic adhesive | -40 °C to +10 °C | Good UV and weather resistance, flexible at low temperatures, suitable for outdoor applications |
| Silicone adhesive | -100 °C to -50 °C | Extremely flexible at low temperatures, very high temperature resistance, ideal for extreme temperatures |
| Rubber adhesive (natural rubber) | -60 °C to -40 °C | Very good immediate adhesion, remains elastic even at low temperatures, but limited heat resistance |
| Synthetic rubber (e.g. hotmelt adhesive) | -30 °C to -10 °C | Good adhesion to difficult surfaces, but less cold-resistant than natural rubber |
| Epoxy adhesive | +50 °C to +150 °C | Very high mechanical strength, extremely heat-resistant, but often brittle at low temperatures |
| Polyurethane adhesive (PU) | -50 °C to -20 °C | Elastic at low temperatures, high resistance to moisture & chemicals |
| Phenolic resin adhesive | +100 °C to +250 °C | Very heat-resistant, frequently used in high-temperature applications such as aviation or the automotive industry |
Materials for cold and heat-resistant adhesive tapes
In order to understand the influence of extreme temperatures on adhesive tape, it is important to first understand the structure of adhesive tape. Adhesive tape rolls consist of 5 components or layers, two of which are essential for
- Tear resistance and stretchability/flexibility (backing material) and
- Adhesive strength, immediate adhesion or durability(adhesive or the adhesive mass).
In the following, we will therefore look at the different types of backing material and adhesive types in relation to their temperature resistance.
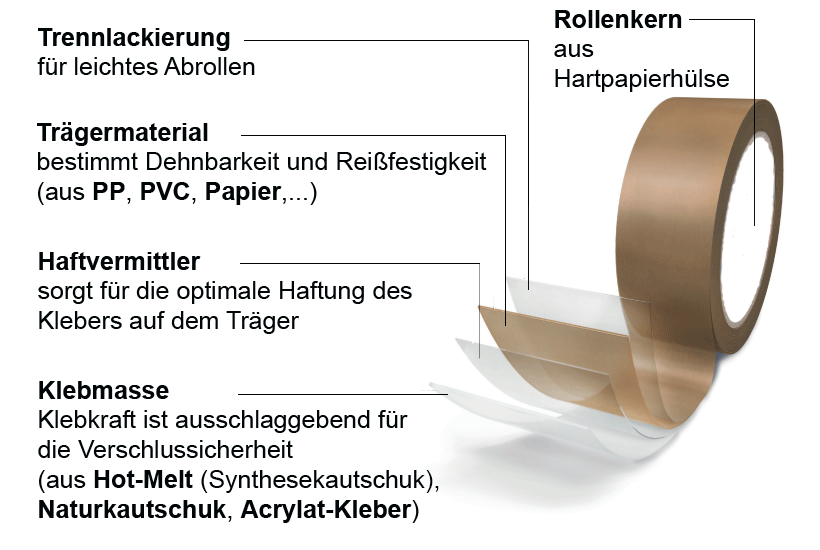
Backing materials
The backing material of an adhesive tape significantly influences its resistance to extreme temperatures. It not only has to withstand mechanical stress, but also maintain its structure and adhesion in hot or cold conditions. Heat-resistant materials such as polyimide (e.g. known as Kapton® from DuPont), PTFE (e.g. known as Teflon™ from Chemours) or aluminium foil are particularly suitable for environments with high temperatures, as they do not melt or deform. Polyimide tapes are used in electronics, for example, as they can withstand temperatures of up to 300 °C without losing their insulating properties. PTFE adhesive tapes are chemically resistant, non-adhesive and heat-resistant up to around 260 °C, making them ideal for applications in the aviation or chemical industries. Aluminium foil adhesive tapes reflect heat and are often used in the insulation or protection of heat-sensitive materials.
On the other hand, cold-resistant adhesive tapes must remain flexible and must not become brittle. PVC carriers can also be used at sub-zero temperatures due to their elasticity and are used in the construction and packaging industries. Polyester backings are particularly resistant to low temperatures, UV radiation and moisture, which makes them ideal for outdoor applications or vehicle construction. Fabric or non-woven substrates are another option, as they offer good conformability and do not break easily in cold conditions. The choice of backing material therefore depends heavily on the requirements of the area of application – in particular whether the temperature resistance is required for a short or long period of time.
Heat-resistant backing materials:
- Polyimide: Withstands temperatures up to 300 °C, ideal for electronics
- PTFE: Heat-resistant, chemical-resistant and non-sticky
- Aluminium foil: Reflects heat, ideal for thermal protection
Cold-resistant carrier materials:
- PVC: Good flexibility even at sub-zero temperatures
- Polyester: Resistant to low temperatures and moisture
- Fleece & fabric: Elastic and adaptable in cold conditions
Adhesive types
In addition to the backing material, the adhesive plays a decisive role in the temperature resistance of an adhesive tape. Adhesives react differently to heat and cold – some become soft at high temperatures and lose their adhesive strength, others harden in the cold and can become brittle. Acrylic adhesives are one of the most versatile options as they remain stable at both high temperatures up to 150°C and low temperatures down to -40°C. They adhere well to different surfaces and are particularly weather-resistant, making them suitable for outdoor use. However, they often require a longer curing time than other adhesives.
Silicone adhesives offer the highest temperature resistance and can withstand temperatures from -50 °C to 260 °C. They also remain flexible and adhere reliably to difficult surfaces such as silicone, PTFE or rough metals. This makes them ideal for applications in the aerospace, electronics or automotive industries where extreme temperature changes occur. Rubber and resin adhesives, on the other hand, are particularly flexible at low temperatures and adhere immediately with high initial tack. However, they are only heat-resistant to a limited extent – usually up to a maximum of 70 °C. They are therefore particularly suitable for applications where high instant adhesion is required in cold environments, for example in packaging or the construction industry.
The right choice of adhesive is essential to ensure that the tape works reliably under the respective temperature conditions. While silicone adhesives are recommended for extreme temperatures, acrylic adhesives are a universal solution, and rubber adhesives offer excellent adhesion in cold conditions but low heat resistance.

Acrylic adhesives:
✔ Very temperature resistant (-40 °C to +150 °C)
✔ Resistant to UV radiation and moisture
✘ Often requires a longer curing time
Silicone adhesive:
✔ Extremely temperature-resistant (-50 °C to +260 °C)
✔ High flexibility on difficult surfaces
✘ More expensive than other types of adhesive
Rubber and resin adhesives:
✔ Good adhesion in cold conditions (-30 °C to +70 °C)
✔ Immediately high adhesive strength
✘ Limited heat resistance
Areas of application for cold and heat-resistant adhesive tapes
Industry & mechanical engineering
- High-temperature adhesive tapes for oven applications
- Protection of welding seams from flying sparks
- Cold-resistant adhesive tapes for cooling systems
Electronics & electrical engineering
- Polyimide tape for circuit boards and insulation
- Cold-resistant cable insulation for outdoor use
Automotive industry
- Heat-resistant adhesive tapes for engines & exhaust systems
- Frost-resistant adhesive tapes for vehicle construction in extreme climate zones
Aerospace industry
- Thermally insulating adhesive tapes for extreme temperatures
- Protection of sensitive components at high altitudes
Construction & trade
- Frost-resistant adhesive tapes for outdoor use
- Heat-resistant adhesive tapes for insulation
Which adhesive tapes can withstand which temperatures?
| Backing material | Heat resistance (permanent / short-term) | Cold resistance (application range / material limit) | Typical areas of application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyimide | 260 °C / 400 °C | -60 °C / -269 °C | Electronics, aviation |
| PTFE | 260 °C / 327 °C | -50 °C / -200 °C | Chemicals, industry |
| Aluminium foil | 150-200 °C / 600 °C | -40 °C / -73 °C | Thermal insulation |
| PVC | 60-80 °C / 105 °C | -10 °C / -30 °C | Construction, trade |
| Polyester (PET) | 120-150 °C / 200 °C | -50 °C / -70 °C | Automotive, industry |
The specified temperatures refer to continuous load. Higher or lower temperatures can be tolerated in the short term.
Tips for correct use and storage
- Acclimatise adhesive tapes before use so that they achieve optimum adhesion
- Clean and dry surfaces to ensure maximum adhesive strength
- Do not use heat-resistant adhesive tapes in a direct flame, only as protection
- Do not stretch cold-resistant adhesive tapes too much, otherwise they may become brittle
- Store adhesive tapes in a dry place with UV protection to prevent material ageing
Further details on the temperature resistance of various materials can be found in our reference article: How does plastic behave in heat?
More about the structure and different types of adhesive tape: Types of adhesive tape – what are adhesive tapes made of?
Do you want to know which adhesive tape is particularly suitable for which surface? Adhesive tape on different surfaces: What do you need to look out for?
Also helpful: The guide “Bonding – but the right way“, developed in co-operation with the Industrieverband Klebstoffe e.V. and the Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM.
✅ Discover the right adhesive tape for extreme temperatures now!














