Consumers are not yet fully aware of it, but reusable transport packaging is becoming more and more common. Its popularity lies precisely in this so-called “reusability”. It is the key concept for more sustainable logistics. Find all the information on this trend here and do something for the environment and your business.
1. What is reusable transport packaging?
Les emballages de transport réutilisables sont souvent appelés RTP, l’abréviation anglaise de Returnable Transport Packaging. Un RTP est un emballage utilisable plusieurs fois. Contrairement aux emballages jetables, un RTP est simplement lavé, empilé et retourné à l’entreprise d’origine de façon à être réutilisé. Les palettes plastique, les bacs navettes ou les caisses-palettes en sont des exemples.
Les emballages réutilisables sont utilisés dans de plus en plus de secteurs comme l’alimentation, l’automobile, la chimie et la distribution pour ne citer qu’eux. Les RTP sont généralement en bois, en métal ou en plastique. Certaines variantes, comme les palettes en bois, passent d’une entreprise à l’autre car elles possèdent des dimensions standard. Les autres emballages appartiennent eux, à une société spécifique et restent donc dans un cycle interne (p. ex. les bacs navettes).1
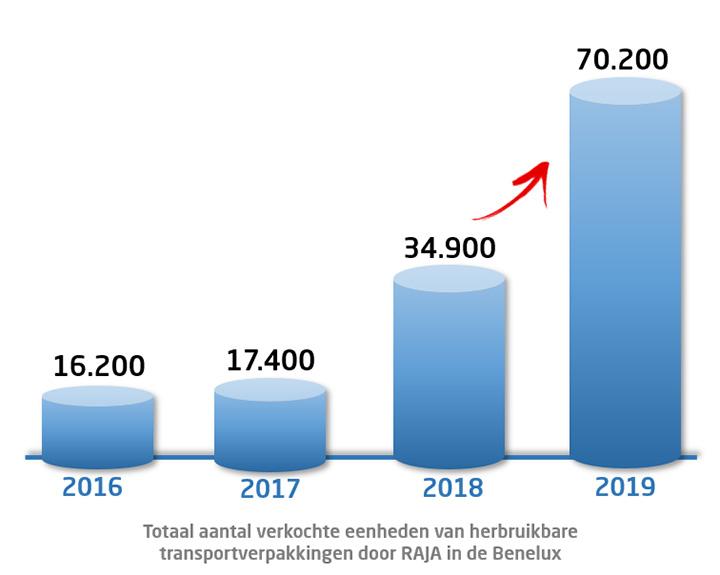
► Save money and space
[Thereare two advantages to using an RTP. The first is financial: reusable packaging is more expensive than disposable packaging, but these extra costs quickly turn into benefits because an RTP is used much more often.
The second advantage is logistical: an RTP is usually made of lightweight materials, which reduces CO2 emissions during transport. In addition, the dimensions of these packages are perfectly matched to each other. The result? You move more packages per transport.

► Pack faster and safer
With an RTP, you can pack your products much more easily and quickly. With a reusable shuttle box, for example, you no longer need crates, strapping, adhesive tape, or even packaging film, etc. Unlike disposable packaging, an RTP can be opened and closed several times to check the contents without damaging its transport packaging.
Finally, reusable transport packaging is made of strong materials (which gives it a longer lifespan), so your products are better protected in the event of difficult transport

► A sustainable alternative
‘Circularity’ is the word of the future. By closing the material cycle, waste production and the use of raw materials is reduced.2 Many RTPs are made of, among other things, PP and PE plastic, both of which are easy to recycle and can be recycled several times.
Reusable transport packaging significantly reduces the amount of waste produced by the logistics sector. A well-maintained RTP can be used dozens or even hundreds of times.
3. Some commonly used RTPs

| Type of RTP |
Characteristics and use |
| (1) Wooden or plastic pallets |
– Suitable forexport (according to ISPM15)– Perfectly stackable– Forthe transport of large quantities of goods |
| (2) Pallet boxesmade of plastic (PP) | – Smooth interior protects the contents of the box– Ideal for the non-food supply chain: sports equipment, textiles, clothing, etc.– Forstorage and transport of light to +/- heavy goods. |
| (3)Plastic (PP) shuttle bins |
– Ideal for internal transport cycle– Perfectly stackable and nestable for maximum space saving when shipping empty– For the transport of small goods to another location. |
| (4)Plastic stacking bins (PP) |
– Maximum use of space: to be combined with other stacking bins or Euro pallets– For the storage or transport of light or small goods. |














