Storage methods, equipment needed, audits of greater or lesser frequency, applicable standards and regulations…. How many elements to bear in mind when organising your warehouse and properly optimising the associated flows and safety.
You don’t need to look any further: we have created a complete guide to all the most important principles that will help make your warehouse a place that is truly suited to your business.
CONTENTS
- The ABC method
- Flow optimisation: LIFO and FIFO
- Optimisation of box layout: prerequisite for choosing storage method
- How do I choose the right storage method?
- High-rotation storage on racks/shelves in aisles
- Mezzanine floor storage
- Storage on pallets with extensions
- Storage on pallets in aisles according to the traditional method
- High bay storage (narrow aisles)
Basic storage principles
In order to organise the work of a warehouse well, you must first choose a storage method that will help you optimise the flow of goods and operators, resulting in increased productivity.
So let’s start by reviewing the different methods available, as well as ways to make it easier to choose the method suited to your business.
The ABC method
Are you familiar with the Pareto principle? If so, you are already familiar with the basic principle of the ABC method, which helps to stock products according to their turnover rate.
When applied to logistics, the Pareto principle states that 20% of the stored goods represent 80% of the total stock.
This is why the ABC method consists of storing products in a warehouse according to their renewal rate over a given period of time.
To implement this method, it is first necessary to calculate the stock turnover rate in the warehouse. This can be done by calculating the ratio of releases from the warehouse to the corresponding average stock.
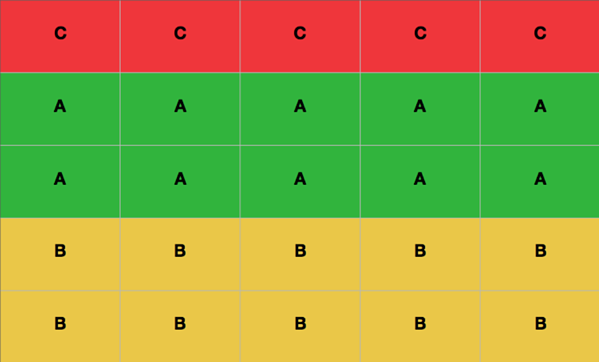
You then select the products to be included in categories A, B and C:
- Category A corresponds to that famous 20% of goods that are subject to 80% turnover. These products must be at the height most convenient for order preparers to pick.
- Category B corresponds to 15% turnover and 30% goods. These products, which leave the warehouse less frequently, can be located at the bottom of the shelves.
- Category C corresponds to 5% of the turnover and 50% of the stock. Products in this category, which rarely leave the warehouse, should be placed at the top of the shelves.
It is also possible to organise the warehouse itself according to the ABC method, not just to distribute the goods in the various locations on the racks or shelves. The aim is then to optimise the picking flows carried out by the operators.
Category A products, with very high rotation, will then be located near the order preparation area. As we move further into the warehouse, we will pass goods with decreasing rotation: first from category B and then from category C.
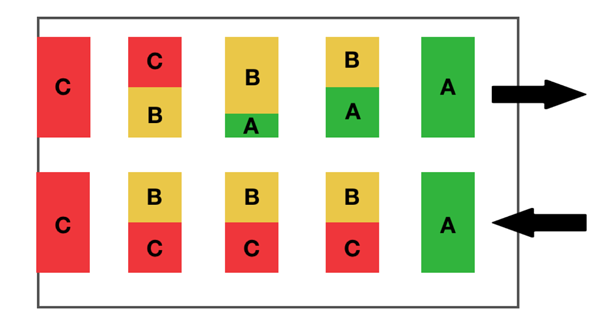
This is the first storage method chosen by many warehouses to optimise the distribution of goods.
Flow optimisation: LIFO and FIFO
The next storage methods worth knowing are those called LIFO and FIFO.
These are two opposing storage methods, each associated with a specific accounting method.
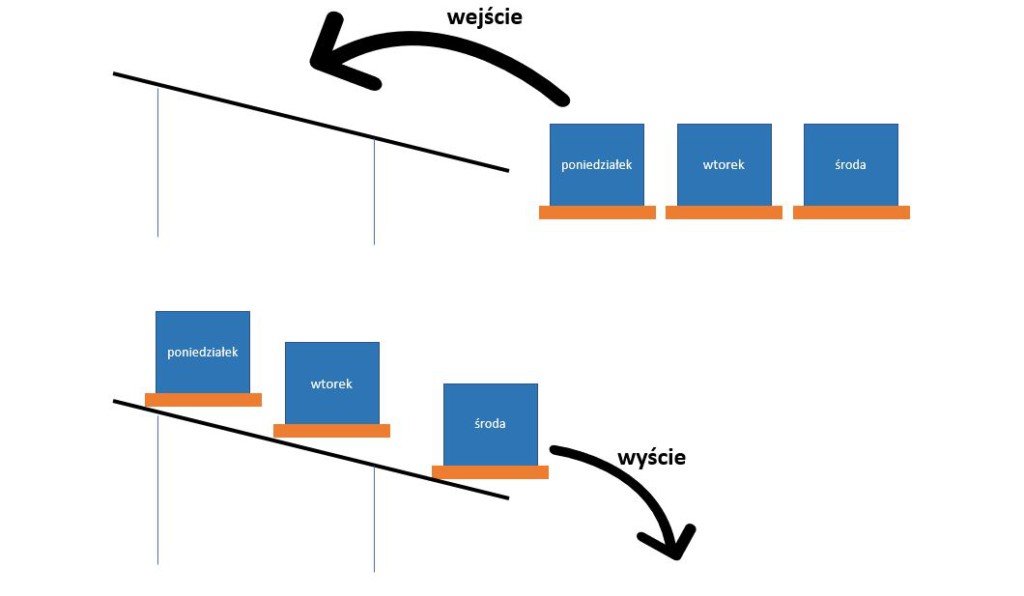
According to the LIFO method, which stands for Last In First Out, the products that enter the warehouse last are placed closest to the packing area. As the name suggests, the aim is to get these goods out more quickly in order to optimise warehouse flows.
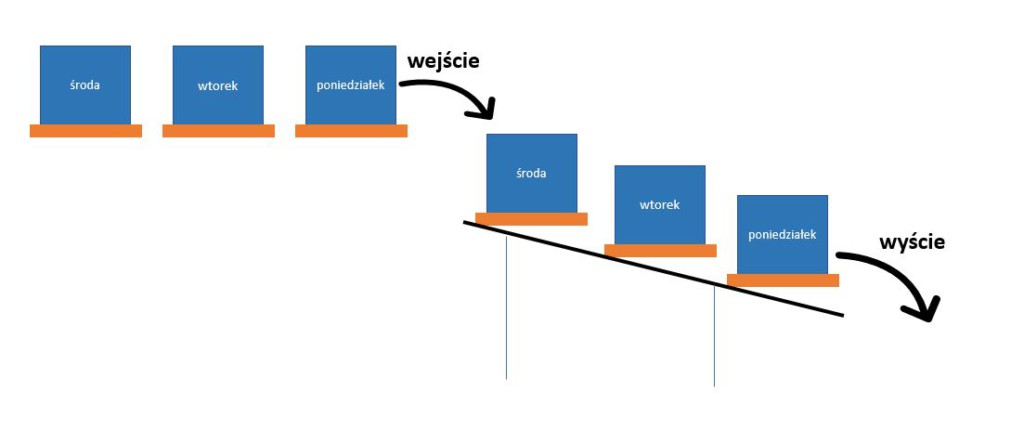
FIFO method. First In First Out (FIFO) is the opposite of the first method. Products entering the warehouse earlier are stored near the packing area so that they are close at the time of release and their flows are optimised.
You already know the 3 key methods for organising a warehouse. So how do you choose the one that best suits your specific situation?
Optimising the arrangement of boxes: a prerequisite for choosing a storage method.
Whichever method you choose, you must first optimise the arrangement of the boxes. Aim: to check the available space in the warehouse.
Depending on the type of handling, you should leave smaller or larger gaps between crates:
- If you use manual handling, operators only need a few centimetres above the crates and on the sides.
- If the warehouse is operated by machines, a minimum gap of 10 centimetres should be left.
In any case, the aim is to find the perfect balance between limiting the space between boxes and the speed of the operators picking the products. By keeping this in mind, you are able to choose the storage method that really suits your business and type of warehouse.
How do I choose the right storage method?
It is now necessary to choose the right storage method for the type and rotation of goods stored.
If you sell products with a short shelf life, with a best-before date or use-by date, it is necessary to choose the FIFO method. This is the only method that allows you to release the goods that have been in stock the longest first.
However, you can combine the FIFO method with the ABC method in order to optimise the picking carried out by the operators and reduce their movement around the warehouse.
For any other type of activity, you should focus on the ABC method.
Before embarking on such a reorganisation, it is a good idea to carry out a preliminary audit to help you properly assess your stock:
- This involves determining the quantity, size and weight of products stored over the last 12 months. Later in this article, this will be used to determine what type of shelving or racking best suits your needs.
- You should identify the goods that account for 80% of your turnover and use the ABC method described above.
- If your warehouse flows are characterised by seasonality, it should be reorganised with this in mind. Some products, ordered in bulk during a given season, will have to be moved from category B or C to category A in order to optimise picking flows.
Note: If your warehouse has high-bay shelving, always remember to have an expert assess the strength of the floor or concrete slab. The regulations prescribe that the racks must be anchored to the ground.
Let us now turn to an overview of the different types of storage you can use.

The different types of storage
You can choose the right equipment depending on the method you choose as well as the type of products to be stored. Below we list 5 typical types of storage from which you can choose the one that best suits your needs.
High-rotation storage on racks/shelves in aisles
This type of storage, as its name suggests, is designed for warehouses for products with a high turnover of goods, particularly those using the FIFO method.
We find there:
- High-rotation products close to the packing area, at the most accessible height;
- Low-rotation products deep in the aisles.
Goods are stored according to their weight: the heavier they are, the lower they are placed on the racks or shelves.
For ergonomic reasons, remember to limit the height of the shelves to a maximum of 2 metres.
What accessories will be necessary?
- When it comes to shelving, choose:
- Inclined or horizontal shelving for small and medium-sized warehouses;
- Mixed shelving, to optimise space, for larger warehouses. With these racks, it is possible to simultaneously store pallets at height and products for picking at operator level.
- To optimise picking, equip yourself with:
- Workshop containers for the smallest products;
- Crates with horizontal opening or lockable doors for the largest products.
Mezzanine floor storage
This type of storage is based on the same principle as the previous one, except that the warehouse is divided into two independent floors.
The two separate areas allow for the creation of independent installations with shelving, storage areas and even office space.
The idea here is to ensure that the poles take up as little space as possible in order to optimise the storage of goods. The movement of vehicles such as order pickers or pallet trucks on the floor must also be taken into account here.
What accessories will be necessary?
- The building material for the mezzanine floor should be carefully selected to ensure the highest possible safety.
- To this end, you should also think about safety barriers around the pillars and at the entrance to the mezzanine floor.
- Marking tapes and other types of signage are required to comply with signage regulations.
Storage on pallets with extensions
This method of storage will mainly be suitable for products:
- Which cannot be packed on a pallet,such as pipes or carpets;
- That are highly seasonal.
It is a more flexible storage system than bulk storage.
What accessories will be necessary?
- You will need pallets with galvanised extensions placed inside or outside.
Palletised aisle storage according to the traditional method.
This is the most common method of storage in pallet warehouses, particularly those operating on a B2B basis.
Before storing these pallets, their characteristics must be properly defined. It is necessary to note their dimensions, load, direction of retrieval, as well as the height of the first level and adjust the racks accordingly.
What accessories will be necessary?
- You will need pallet racks adapted to the specific characteristics of the pallets: choose the best from the large range of racks available.
- Safety rails must also be fitted to the racks.
- It is also necessary to signpost the warehouse and place mirrors in the warehouse to improve the visibility of operators and increase traffic safety.
Storage on high racks (narrow aisles)
If the height of the racks exceeds 7 metres, it is necessary to use the high storage method. This method is particularly suited to warehouses with high logistical capacity.
In these narrow aisles, guides for forklift operators are installed, forcing the use of stringers at the bottom of the forklift. This is mandatory because storage on the ground is impossible.
This method of storage requires forklifts moving in three directions, which avoids blocking the forklift and ensures maximum use of the aisle width.
What accessories will be necessary?
- Guides on the ground;
- Additional racking modules;
- Protection for additional modules and column protection in the aisles;
- Pallet stops;
- Safety nets;
- Built-in sprinkler system;
- Signage and load boards.
Now you are ready to implement the optimum storage method to gain more space, increase efficiency and safety in your warehouse.
If you need assistance in selecting your warehouse equipment items, please contact us via tel: 801 55 3000* or e-mail: poczta@rajapack.pl. Our specialists will help you choose the best packaging solutions to suit your business.















